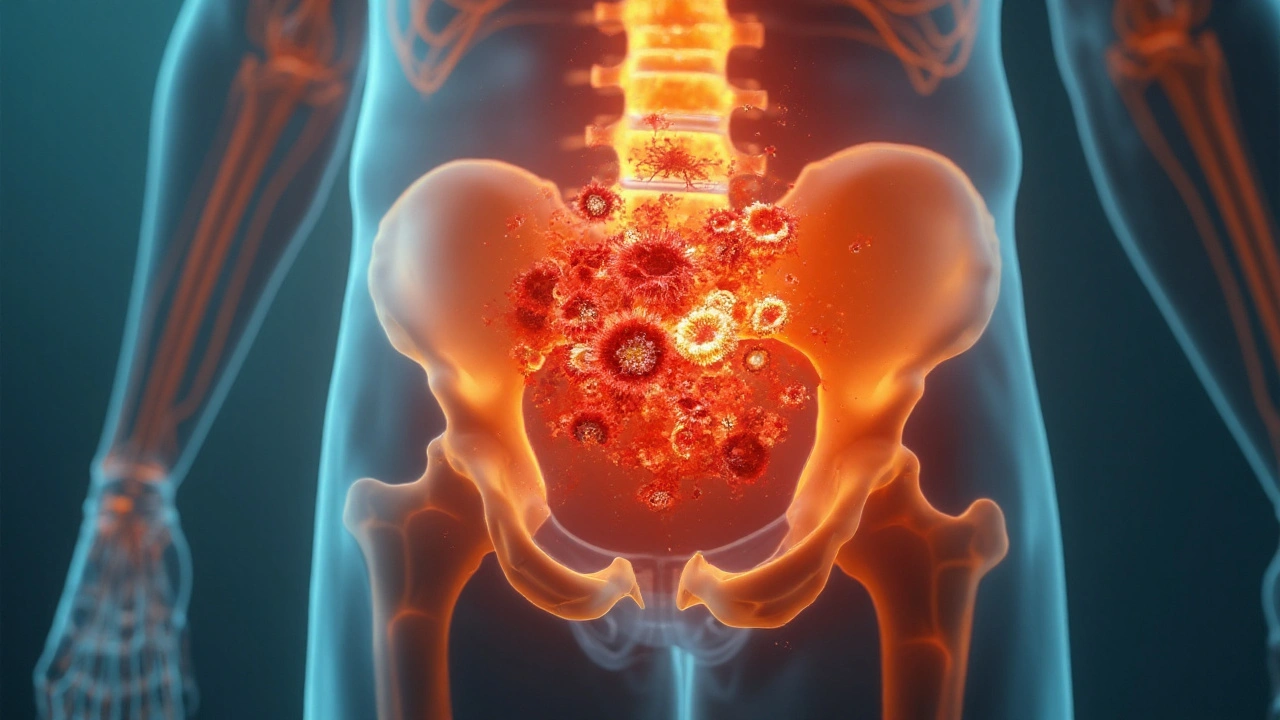
Explore how bone marrow disorders like MDS, aplastic anemia, and myeloproliferative neoplasms increase the chance of developing blood cancers, with stats, mechanisms, and monitoring tips.
Read MoreCancer Risk: Understanding, Reducing, and Monitoring
When talking about Cancer Risk, the probability that an individual will develop cancer over a specified time frame. Also known as cancer probability, it is shaped by a mix of biology and daily habits. One of the biggest drivers is Genetic Factors, inherited gene mutations that increase susceptibility to certain cancers. Another core piece is Lifestyle Choices, behaviors such as diet, tobacco use, alcohol consumption, and physical activity that can either raise or lower that probability. Environmental Exposures, contact with carcinogens like asbestos, UV radiation, or polluted air also play a crucial role. Finally, Screening Programs, regular medical tests that catch early signs before symptoms appear provide a practical way to keep risk in check. In short, cancer risk depends on what you inherit, what you do, and what you’re exposed to, but early detection can shift the odds in your favor.
Key Factors Influencing Cancer Risk
Genetic factors influence cancer risk by setting a baseline vulnerability; for example, BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations dramatically increase breast and ovarian cancer chances. Lifestyle choices modify that baseline—smoking adds carcinogens to the lungs, while a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and fiber can provide protective antioxidants. Environmental exposures interact with both genetics and lifestyle, as pollutants may trigger DNA damage that overwhelms the body’s repair mechanisms, especially in people with weaker genetic defenses. Screening programs counteract these risks by spotting precancerous changes early, which allows for less invasive treatments and better outcomes. Together, these elements create a network where genetics, behavior, and environment shape the overall probability of developing cancer, and proactive screening can break the chain before it leads to disease.
Below you’ll find a curated set of articles that dig deeper into each of these areas—comparisons of medications that might affect risk, practical tips for managing side effects, and guidance on choosing safe online pharmacies for preventive supplements. Use these resources to build a personal plan that tackles the biggest contributors to your cancer risk while staying informed about the latest preventive tools.