Learn how rate control, rhythm control, and stroke prevention work together in atrial fibrillation treatment. Discover which approach is right for you based on age, symptoms, and risk factors.
Read MoreRate Control: Managing Heart Rate in Atrial Fibrillation and Other Arrhythmias
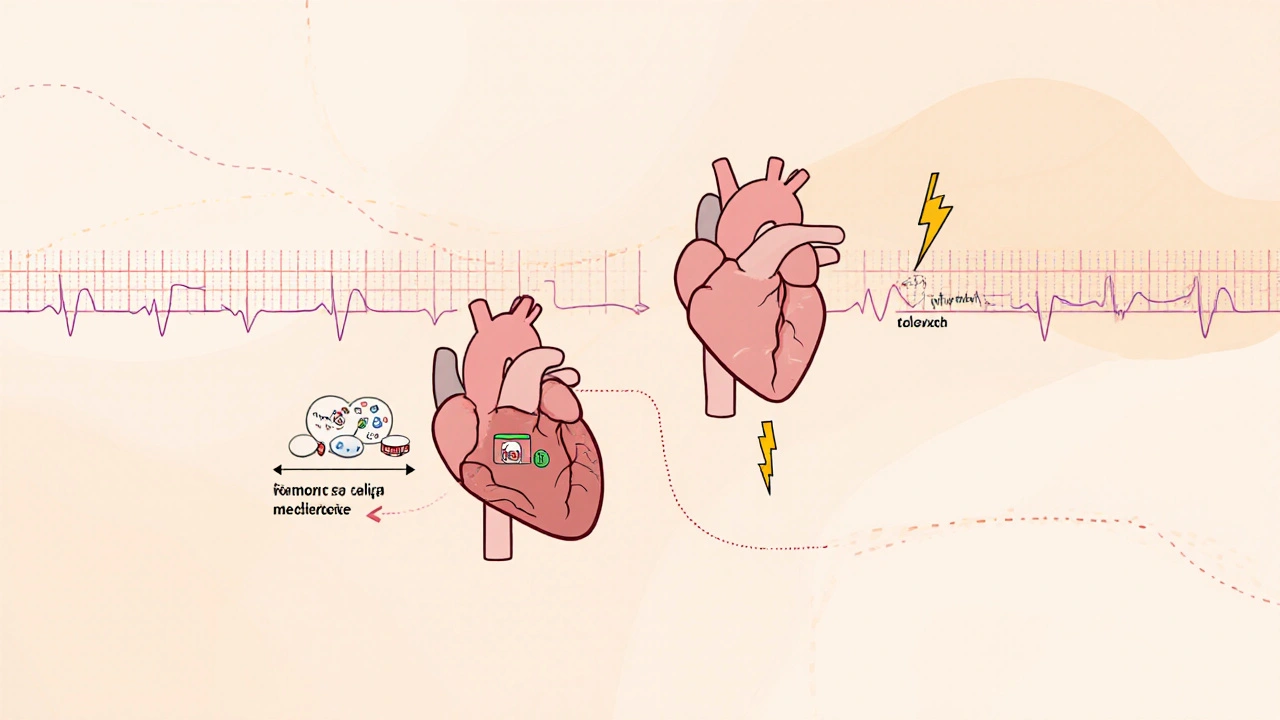
When your heart races out of control—especially with atrial fibrillation, a common irregular heartbeat where the upper chambers quiver instead of pumping properly—you don’t always need to restore a normal rhythm. Sometimes, the goal is simpler: rate control, a treatment approach focused on slowing down the heart rate to a safe level. It’s not about fixing the rhythm. It’s about keeping you from feeling awful, avoiding heart damage, and staying out of the hospital. Many people live well with atrial fibrillation as long as their heart doesn’t beat too fast, and that’s where rate control steps in.
Doctors use a few main tools to do this. beta blockers, medications that block adrenaline’s effect on the heart, are often the first choice. Drugs like metoprolol or atenolol gently slow the heart, reduce palpitations, and lower blood pressure. If those don’t work or cause side effects like fatigue or dizziness, calcium channel blockers, drugs like diltiazem or verapamil that reduce the electrical signals in the heart are next. These work differently than beta blockers but target the same problem: too-fast heartbeats. Some patients even get digoxin, especially if they have heart failure along with atrial fibrillation. The key is finding the right balance—slow enough to feel better, but not so slow that you get dizzy or tired all the time.
Rate control isn’t just for atrial fibrillation. It shows up in other rhythm problems too, like supraventricular tachycardia or even some cases of heart failure where the heart is overworked. What matters isn’t the exact diagnosis—it’s whether your heart is racing beyond what your body can handle. Studies show that for most people with chronic atrial fibrillation, rate control works just as well as trying to restore normal rhythm, with fewer side effects and less need for procedures. You don’t need to be perfect. You just need to be stable.
What you’ll find in the posts below are real-world guides on how these medications work, how they compare, and what to watch out for. You’ll see how rate control fits into broader treatment plans, how it interacts with other drugs like anticoagulants, and why some people do better on one pill than another. There’s also advice on monitoring your heart rate at home, spotting warning signs, and talking to your doctor about what’s working—or not. This isn’t theory. These are the stories and facts that help real people manage their condition day to day.