A thorough comparison of Serophene (Clomiphene) with letrozole, tamoxifen, gonadotropins and other fertility options, covering mechanisms, success rates, side effects, costs and practical tips.
Read MoreClomiphene – Basics, Benefits, and FAQs
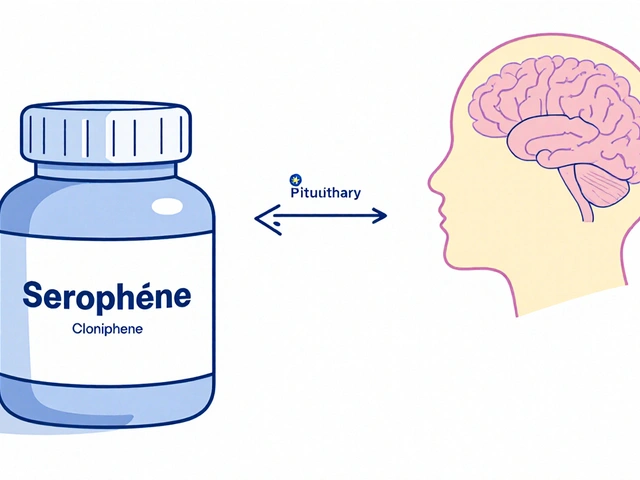
When talking about Clomiphene, a selective estrogen receptor modulator used to trigger ovulation. Also known as Clomid, it’s prescribed mainly for infertility, the inability to conceive after regular, unprotected intercourse and for Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), a hormonal disorder that disrupts ovulation. Doctors also refer to its use as ovulation induction, the process of stimulating the ovaries to release eggs. Below you’ll see why these links matter and how they shape the articles you’ll find further down.
First off, Clomiphene belongs to the class of drugs called selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs). That means it blocks estrogen receptors in the brain, tricking the pituitary gland into thinking estrogen levels are low. The gland then releases more follicle‑stimulating hormone (FSH), which nudges the ovaries to grow follicles and eventually release an egg. In plain language, it’s like pulling the brakes on estrogen so the body speeds up egg production. This mechanism makes it a go‑to option for women who don’t ovulate regularly, whether it’s due to PCOS, unexplained infertility, or secondary amenorrhea.
When to Choose Clomiphene and What to Expect
Most fertility specialists start with Clomiphene because it’s inexpensive, oral, and backed by decades of data. Typical treatment begins on day 3‑5 of the menstrual cycle, with a low dose that can be increased each month if ovulation doesn’t occur. Success rates hover around 15‑20% per cycle for general infertility and up to 25% for PCOS‑related cases. That’s why many of our posts compare Clomiphene to newer agents like letrozole, discuss dosing strategies, or explain how to monitor ovulation with home LH kits. If you’re curious about side effects, the common ones include mild hot flashes, mood swings, and occasional visual disturbances—most resolve once the medication stops.
Beyond the basics, the tag collection also dives into practical issues: how to combine Clomiphene with intrauterine insemination (IUI), what to do if you experience multiple pregnancies, and how to handle a failed cycle. One article walks through a step‑by‑step plan for tracking basal body temperature, while another outlines when to switch to injectable gonadotropins if Clomiphene isn’t enough. These pieces help you move from “what is it?” to “how do I use it safely and effectively?” without a PhD in reproductive endocrinology.
Another hot topic we cover is the myth that Clomiphene is only for women. While the primary indication is female infertility, male doctors sometimes prescribe it off‑label to boost testosterone in hypogonadal men. That crossover is explained in a concise guide that outlines dosage differences, monitoring labs, and potential risks. It shows how a single drug can touch multiple health areas, reinforcing the idea that understanding its pharmacology pays off across genders.
Our posts also address the emotional side of fertility treatment. Dealing with cycle failures, hormonal swings, and the pressure of timed intercourse can wear anyone down. We’ve written pieces on coping strategies, partner communication, and even how to keep a fertility journal. By weaving the science of Clomiphene with real‑world advice, the collection aims to be a one‑stop resource for anyone navigating the ups and downs of trying to conceive.
Finally, you’ll find articles that compare Clomiphene to other infertility drugs, break down insurance coverage nuances, and explain the latest research on long‑term safety. Whether you’re a first‑time user, a seasoned patient, or a healthcare professional looking for a quick refresher, the range of topics covered here reflects the full spectrum of questions people ask about this medication.
Ready to dig deeper? Below is a curated list of articles that unpack Clomiphene’s uses, dosing tips, side‑effect management, and comparisons with alternative therapies. Each piece is written to give you clear, actionable info you can apply right away.