Learn how novel influenza strains strain hospitals and discover practical steps to manage beds, staff, PPE, and vaccines during outbreaks.
Read MoreSurge Capacity: Managing Unexpected Demand in Healthcare
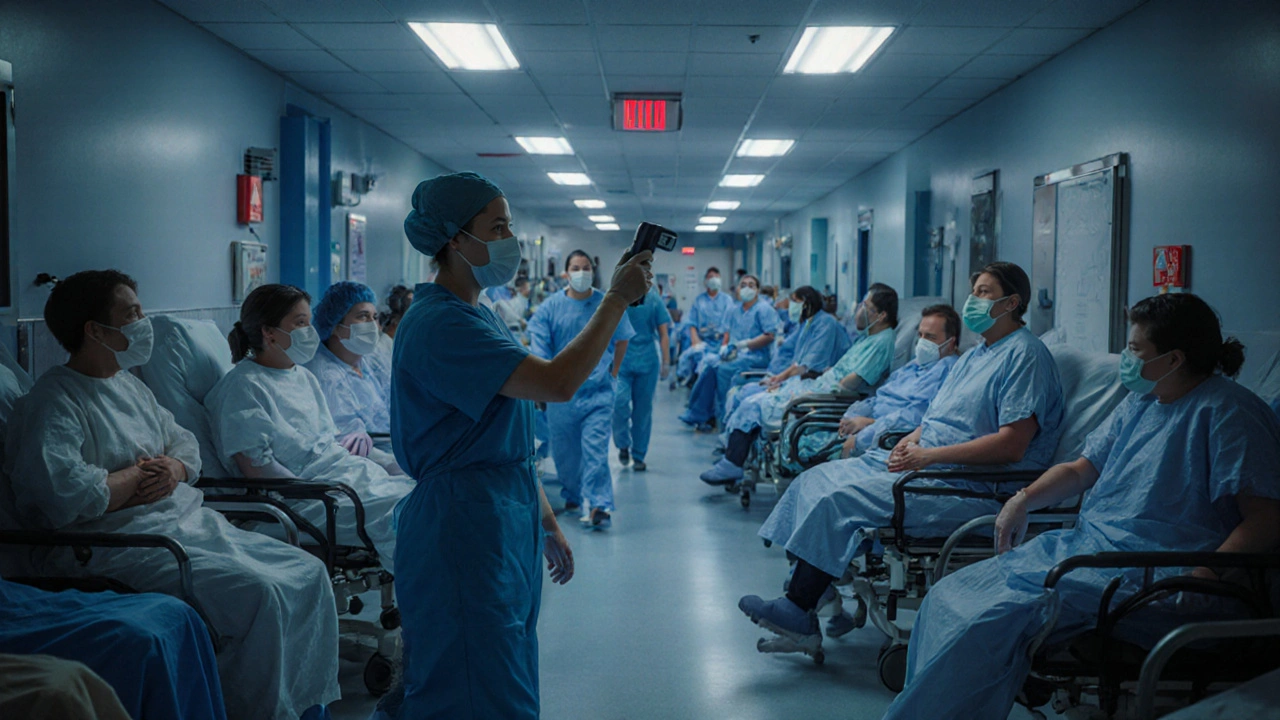
When dealing with Surge Capacity, the ability of a health system to quickly expand services during spikes in patient volume. Also known as capacity surge, it becomes the backbone of any emergency or pandemic response. Think of it as a safety valve that lets hospitals, clinics, and public health agencies absorb a sudden influx of patients without crashing. Without a clear plan, a brief outbreak can overwhelm beds, staff, and supplies, turning a manageable situation into a crisis.
Why Surge Capacity Matters
Imagine a flu season that doubles the typical patient load in a week. Surge capacity is what lets a hospital add extra beds, open new wards, and reassign staff fast enough to keep care flowing. It’s not just about space; it’s about Hospital Surge Capacity, the specific strategies hospitals use to expand bed count, ICU capability, and equipment availability. That includes converting recovery rooms into ICU units, borrowing ventilators, or setting up temporary field hospitals. When hospitals have a solid surge plan, they can keep critical services running while the surge tapers off.
But beds alone won’t solve the problem. Medical Staffing, the pool of doctors, nurses, and support personnel ready to be redeployed during high‑demand periods is a crucial piece of the puzzle. Staffing flexibility means cross‑training nurses for ICU duties, activating on‑call physician rosters, and even tapping qualified volunteers. Effective staffing hinges on clear communication, rapid credential verification, and burnout prevention—otherwise the workforce itself becomes a bottleneck.
Every extra bed and extra staff member needs the right equipment, medication, and protective gear to work. That’s where Resource Allocation, the process of distributing limited medical supplies, drugs, and devices where they’re needed most comes in. Smart allocation uses real‑time data dashboards, predictive modeling, and predefined priority tiers (for example, reserving ventilators for patients with the highest chance of recovery). When resources are allocated transparently, it builds trust among clinicians and the community.
All these elements—beds, staff, supplies—feed into a broader Emergency Response, the coordinated actions taken by health systems, government agencies, and NGOs during a public health crisis. An effective emergency response integrates surge capacity planning with communication strategies, public health surveillance, and recovery plans. It’s a cycle: anticipate the surge, mobilize resources, manage the peak, then return to normal while learning from the experience.
Below you’ll find a curated set of articles that dive deeper into each of these topics. From practical guides on expanding ICU space to tips on safely buying generic medications online, the collection shows how surge capacity touches every corner of health care. Keep reading to explore real‑world examples, step‑by‑step instructions, and the latest tools that can help you or your organization stay ready when demand spikes.